Your Temporal muscle atrophy dog images are ready. Temporal muscle atrophy dog are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Temporal muscle atrophy dog files here. Get all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for temporal muscle atrophy dog pictures information connected with to the temporal muscle atrophy dog topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website always provides you with hints for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
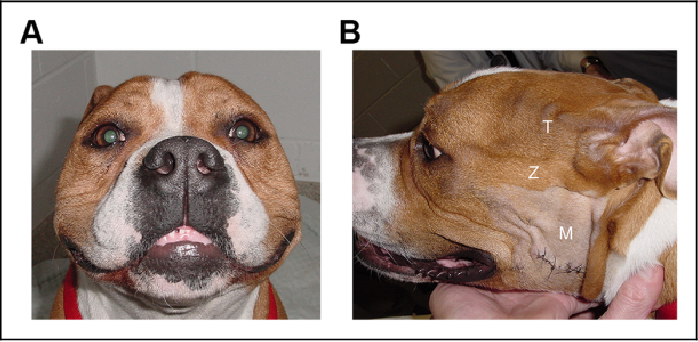
Temporal Muscle Atrophy Dog. Clinical examination showed atrophy of the right temporalis and masseter muscles. Severely affected dogs may present with dysphagia may have growth retardation megaoesophagus lameness and widespread muscle atrophy. Electromyographic changes indicating myopathy and involving both the temporalis and cranial tibial muscles were observed in two of the dogs in group A seven of those in group B and in all the dogs in group C. The condition is not usually pruritic nor painful.
 Comparative Neuromuscular Laboratory From vetneuromuscular.ucsd.edu
Comparative Neuromuscular Laboratory From vetneuromuscular.ucsd.edu
Atrophy illustration relating to dogs including description information related content and more. Right enophthalmos was present but no anisocoria was noted in either a light or darkened room. When atrophy results from an injury or surgery it may be fairly obvious. Human and canine studies show that muscle atrophy selectively affects Type II fast twitch muscle fibres which may account for the decline in speed or performance in older dogs. A problem with muscle function termed a myopathy can result in muscle atrophy. Diagnosis had a significant influence on the type of neurological abnormalities with additional neurological deficits observed in most dogs with pTNST and in all dogs with other extra-axial mass lesions.
Diagnosis is made by history and.
The chemistry panel may show an increase in creatine kinase CK AST and globulins. Muscle atrophy in dogs is the wasting or loss of the dogs muscle tissue. Several muscles in the dogs head area include the temporalis muscle the masseter muscle the pterygoid muscle and the rostral digastricus muscles. A problem with muscle function termed a myopathy can result in muscle atrophy. The atrophy of the temporalis muscles should be differentiated from neuropathies endocrine diseases and cancer cachexia. There is commonly temporal and masseter muscle atrophy.
 Source: midogguide.com
Source: midogguide.com
It often occurs in the legs particularly the hind legs although it can show up in other areas of the body. This disease causes inflammation of the muscles of the jaw and temples causing pain and dysfunction. What Is Muscle Atrophy. The most common cause of temporalis and masseter muscle atrophy in dogs is masticatory muscle myositis MMM which is caused from an immune mediated attack against the muscle fiber. Muscle atrophy is a medical condition when the mass of muscles deteriorates resulting in muscle tissue loss sometimes in localized areas and other times affecting multiple.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Severely affected dogs may present with dysphagia may have growth retardation megaoesophagus lameness and widespread muscle atrophy. Both of these cases presented with. In the acute its most common symptoms are pain and fever. Electromyographic changes indicating myopathy and involving both the temporalis and cranial tibial muscles were observed in two of the dogs in group A seven of those in group B and in all the dogs in group C. It often occurs in the legs particularly the hind legs although it can show up in other areas of the body.
 Source: vetfolio.com
Source: vetfolio.com
Clinical examination showed atrophy of the right temporalis and masseter muscles. Several muscles in the dogs head area include the temporalis muscle the masseter muscle the pterygoid muscle and the rostral digastricus muscles. The atrophy of the temporalis muscles should be differentiated from neuropathies endocrine diseases and cancer cachexia. Although atrophy of these muscles can simply be symptomatic of aging as with all muscles an immune mediated disease called Masticatory Muscle Myositis MMM is often to blame. There is commonly temporal and masseter muscle atrophy.
 Source: vetspecialists.co.uk
Source: vetspecialists.co.uk
When atrophy results from an injury or surgery it may be fairly obvious. This is a UNIQUE form of muscle inflammation because the proteins on these. Right enophthalmos was present but no anisocoria was noted in either a light or darkened room. The muscles of mastication are then palpated with attention to painfulness. Muscle atrophy is a medical condition when the mass of muscles deteriorates resulting in muscle tissue loss sometimes in localized areas and other times affecting multiple.
 Source: europepmc.org
Source: europepmc.org
Atrophy can occur slowly over an extended period of time without being all. Diagnosis had a significant influence on the type of neurological abnormalities with additional neurological deficits observed in most dogs with pTNST and in all dogs with other extra-axial mass lesions. Autoantibodies against 2M muscle fibers are seen in 85-90 of dogs. When atrophy results from an injury or surgery it may be fairly obvious. Pathophysiology Inflammation or degeneration trigeminal nerve loss of trigeminal nerve function loss of sensation to face and mouth loss of motor function to masticatory muscles unable to close jaw masticatory muscle atrophy.
 Source: vetneuromuscular.ucsd.edu
Source: vetneuromuscular.ucsd.edu
Note the closure of the lips and any deformities of them. Neurological signs only progressed in 1 dog. 1 with or without restricted. Masticatory myositis is an immune-mediated disorder that affects the Type 2M muscle fibers of the muscles of mastication in the canine. Schirmer Tear Test STT was 0.
 Source: mspca.org
Source: mspca.org
When atrophy results from an injury or surgery it may be fairly obvious. The jaw could be voluntarily closed by the dog. A seven-year-old male neutered labrador was referred to the Queens V eterinary School Hospital QVSH due to bilateral temporal muscle atrophy over a. Pathophysiology Inflammation or degeneration trigeminal nerve loss of trigeminal nerve function loss of sensation to face and mouth loss of motor function to masticatory muscles unable to close jaw masticatory muscle atrophy. Electromyographic changes indicating myopathy and involving both the temporalis and cranial tibial muscles were observed in two of the dogs in group A seven of those in group B and in all the dogs in group C.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
Most dogs should improve with time within 2-10 weeks. The condition is not usually pruritic nor painful. Diagnosis is made by history and. No treatment has shown benefit. The chemistry panel may show an increase in creatine kinase CK AST and globulins.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The disease normally starts with swollen muscles on the top of the head quickly followed by progressive muscle atrophy making opening and closing its mouth difficult and painful and eventually causing the dog to be unable to move its jaw. There is commonly temporal and masseter muscle atrophy. Diagnosis had a significant influence on the type of neurological abnormalities with additional neurological deficits observed in most dogs with pTNST and in all dogs with other extra-axial mass lesions. Electromyographic changes indicating myopathy and involving both the temporalis and cranial tibial muscles were observed in two of the dogs in group A seven of those in group B and in all the dogs in group C. Muscle atrophy in dogs is the wasting or loss of the dogs muscle tissue.
 Source: veteriankey.com
Source: veteriankey.com
But thats not always the case. Clinical examination showed atrophy of the right temporalis and masseter muscles. Right enophthalmos was present but no anisocoria was noted in either a light or darkened room. Electromyographic changes indicating myopathy and involving both the temporalis and cranial tibial muscles were observed in two of the dogs in group A seven of those in group B and in all the dogs in group C. This disease causes inflammation of the muscles of the jaw and temples causing pain and dysfunction.
 Source: cliniciansbrief.com
Source: cliniciansbrief.com
The examination begins with inspection of the head taking special notice of the masseter and temporal muscles for atrophy swelling or asymmetry. The muscles of mastication are then palpated with attention to painfulness. The most common cause of temporalis and masseter muscle atrophy in dogs is masticatory muscle myositis MMM which is caused from an immune mediated attack against the muscle fiber. A problem with muscle function termed a myopathy can result in muscle atrophy. Atrophy illustration relating to dogs including description information related content and more.
 Source: topdoghealth.com
Source: topdoghealth.com
It often occurs in the legs particularly the hind legs although it can show up in other areas of the body. 20 21 For these reasons and because none of the dogs that did not receive medical treatment experienced progression of neurological deficits we currently do not recommend starting empirical treatment when MRI. What Is Muscle Atrophy. A problem with muscle function termed a myopathy can result in muscle atrophy. Schirmer Tear Test STT was 0.
 Source: vetneuromuscular.ucsd.edu
Source: vetneuromuscular.ucsd.edu
Schirmer Tear Test STT was 0. A problem with muscle function termed a myopathy can result in muscle atrophy. Atrophy can occur slowly over an extended period of time without being all. Salivation and the absence of closure of the mouth can be important findings. A complete blood count may reveal a mild nonregenerative anemia and a neutrophilic leukocytosis.

When atrophy results from an injury or surgery it may be fairly obvious. Most dogs should improve with time within 2-10 weeks. A seven-year-old male neutered labrador was referred to the Queens V eterinary School Hospital QVSH due to bilateral temporal muscle atrophy over a. Severely affected dogs may present with dysphagia may have growth retardation megaoesophagus lameness and widespread muscle atrophy. 20 21 For these reasons and because none of the dogs that did not receive medical treatment experienced progression of neurological deficits we currently do not recommend starting empirical treatment when MRI.
 Source: cliniciansbrief.com
Source: cliniciansbrief.com
It often occurs in the legs particularly the hind legs although it can show up in other areas of the body. The adverse effects of prednisolone are well characterized and include muscle atrophy which often predominantly affects the temporalis muscles. Muscle atrophy is a medical condition when the mass of muscles deteriorates resulting in muscle tissue loss sometimes in localized areas and other times affecting multiple. Electromyographic changes indicating myopathy and involving both the temporalis and cranial tibial muscles were observed in two of the dogs in group A seven of those in group B and in all the dogs in group C. The jaw could be voluntarily closed by the dog.
 Source: lawndalevets.com
Source: lawndalevets.com
When all works well your dog has muscle tone and his nerves are effective in relaying information from the brain to the muscles of the head. Muscle atrophy is a medical condition when the mass of muscles deteriorates resulting in muscle tissue loss sometimes in localized areas and other times affecting multiple. Autoantibodies against 2M muscle fibers are seen in 85-90 of dogs. 1 with or without restricted. Although atrophy of these muscles can simply be symptomatic of aging as with all muscles an immune mediated disease called Masticatory Muscle Myositis MMM is often to blame.
 Source: vizslahealth.net
Source: vizslahealth.net
A seven-year-old male neutered labrador was referred to the Queens V eterinary School Hospital QVSH due to bilateral temporal muscle atrophy over a. Right enophthalmos was present but no anisocoria was noted in either a light or darkened room. Masticatory myositis is an immune-mediated disorder that affects the Type 2M muscle fibers of the muscles of mastication in the canine. Note the closure of the lips and any deformities of them. Comparatively facial asymmetry caused by unilateral MM atrophy is observed less frequently and is associated with a limited number of differential diag- noses2Neoplasia of the trigeminal nerve is thought to be the most.
 Source: vetfolio.com
Source: vetfolio.com
Only these muscles are selectively affected. The jaw could be voluntarily closed by the dog. Both of these cases presented with. A seven-year-old male neutered labrador was referred to the Queens V eterinary School Hospital QVSH due to bilateral temporal muscle atrophy over a. Diagnosis had a significant influence on the type of neurological abnormalities with additional neurological deficits observed in most dogs with pTNST and in all dogs with other extra-axial mass lesions.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title temporal muscle atrophy dog by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






